Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming industries around the globe, with automation already reshaping the workforce. While AI brings countless opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and even the creation of new job roles, it's also displacing traditional positions—some of which have been around for decades. As AI continues to evolve, the future of work will undoubtedly look different, with certain tasks and jobs being fully automated.

In this article, we explore 8 jobs that AI will likely replace in the near future and discuss how workers can prepare for a changing employment landscape.
1. Teachers
While teaching is a deeply human profession, AI is gradually making its way into education. Students can learn almost anything by asking popular chatbots like ChatGPT, these chatbots can provide even more detailed answers than what teachers provide. And AI-powered tools like virtual tutors and automated grading systems can help manage administrative tasks and assist students with personalized learning paths. These technologies can deliver personalized lessons based on a student's learning pace, helping to fill in gaps where traditional education might struggle.

Though AI will not replace teachers entirely, many of the tasks teachers do—such as grading assignments, creating lesson plans, and providing general academic support—are likely to be automated. Teachers who adapt to this shift can focus on providing emotional support and cultivating critical thinking skills in their students, areas where human presence remains irreplaceable.
2. Graphic Designers and Photo Editors
AI tools are increasingly reshaping jobs traditionally performed with software like Photoshop. Tools such as OpenAI's DALL-E and MidJourney are capable of generating high-quality images, artwork, and photo edits in seconds based on simple text prompts. What once took hours of meticulous effort—like removing backgrounds, creating visual effects, or designing custom illustrations—can now be achieved almost instantly using AI-powered platforms.

These tools are not only faster but also more accessible, enabling individuals with little to no design experience to produce professional-grade visuals. As a result, entry-level design jobs and routine tasks such as social media graphics, product mockups, and basic photo editing are increasingly being automated, reducing demand for many Photoshop-based roles.
However, AI tools still lack the human touch when it comes to creativity, brand storytelling, and original conceptual design. Skilled graphic designers who focus on creative direction, complex visual storytelling, and mastering niche design styles will remain in demand. By leveraging AI tools as assistants rather than competitors, designers can streamline their workflows and focus on delivering higher-value, innovative projects.
3. Entry-level Programmers
AI is increasingly making its mark in programming, automating tasks that were once carried out by human developers. Tools powered by AI can now write code, identify bugs, and optimize software performance, significantly reducing the need for programmers to handle basic coding tasks. While AI excels at repetitive or less complex programming work, currently it struggles with highly intricate systems and creative problem-solving.
However, the rise of AI has created challenges for those entering the job market. Many computer science graduates now face difficulties finding employment, as entry-level positions are often the first to be automated.
And as AI models continue to upgrade and become more powerful, even experienced programmers are starting to lose their jobs. Last month, it was reported that a software engineer lost his $150K-a-year job to AI and was forced to DoorDash.

To remain competitive, programmers must focus on areas where human expertise remains indispensable, such as software architecture, system design, and solving complex problems that require innovation and strategic thinking.
4. Animators
The animation industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the introduction of AI tools like OpenAI's Sora, a groundbreaking technology capable of generating realistic motion, environments, and high-quality video clips based on text prompts. Sora and similar tools streamline the animation process, automating tasks such as character movements, facial expressions, and environmental rendering, which traditionally required extensive manual effort. Tasks that once required hours of rigging or simulating physics-based movements, can now be accomplished in a fraction of the time through these AI-driven tools.

These tools allow studios to create professional-grade animations faster and at a lower cost, potentially replacing some roles focused on routine animation work. However, while AI excels at replicating realistic motion and automating repetitive tasks, it still lacks the creative intuition, storytelling ability, and unique artistic vision that human animators bring to the table.
To stay relevant in the evolving landscape, animators must focus on mastering creative direction, developing unique visual styles, and embracing AI tools like Sora as assets that enhance, rather than replace, their artistic capabilities.
5. Transportation and Delivery Drivers
With the rise of autonomous vehicles, self-driving trucks, and drones, jobs in transportation and delivery are facing a major disruption. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Amazon are investing heavily in autonomous technologies that could replace human drivers in trucking, ridesharing, and parcel delivery.
China is already at the forefront of implementing this technology in several cities. Companies like Meituan have deployed autonomous delivery robots for last-mile logistics, efficiently navigating urban environments to deliver parcels and food orders.
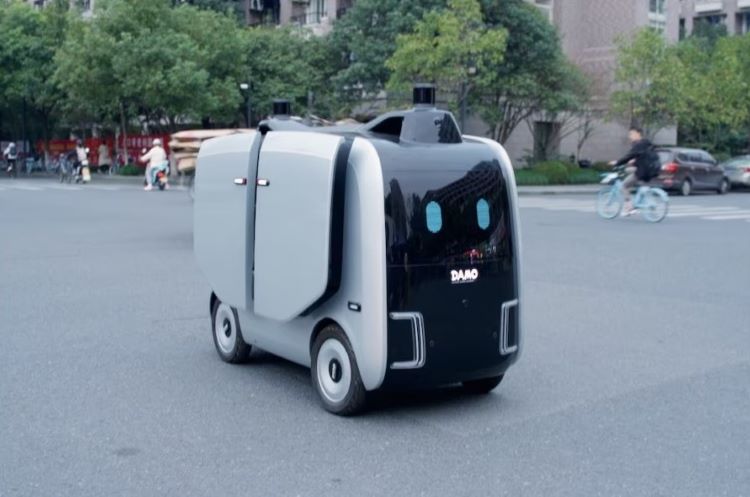

Additionally, drone deliveries are gaining traction, with drones being used to transport goods to hard-to-reach areas, such as remote villages and even tourist spots like the Great Wall. These advancements highlight China's rapid adoption of autonomous technologies, setting a global example for innovative and efficient delivery solutions.
While these technologies are not yet ubiquitous, they are quickly evolving, and millions of jobs in driving and logistics could be replaced by self-driving vehicles. Workers in this field will need to embrace new roles in vehicle maintenance, remote monitoring, and logistics coordination.
6. Warehouse Workers
Automation in warehouses has been on the rise, with robots now handling tasks like picking, packing, and sorting inventory. Companies like Amazon and Walmart have already implemented AI-powered robots to streamline warehouse operations, increasing efficiency and reducing human labor. Recently, advancements in humanoid robots have taken automation a step further. Robots such as Tesla's Optimus and Agility Robotics' Digit are designed to perform tasks with human-like dexterity, making them well-suited for warehouse environments.
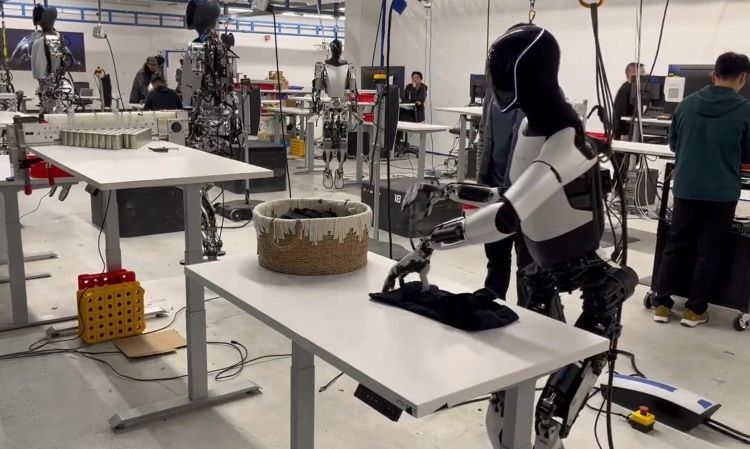

These humanoid robots can navigate complex spaces, lift objects, and adapt to tasks that previously required human workers, further reducing the need for manual labor. While many repetitive tasks will continue to be automated, warehouse workers will still be needed to oversee robot operations, handle non-routine challenges, and manage inventory systems. Workers who adapt by learning to operate and maintain these advanced machines will remain essential in this rapidly evolving landscape.
7. Paralegals and Legal Assistants
AI is already being used in the legal field to automate tasks such as contract review, legal research, and document preparation. AI-powered platforms can quickly analyze legal documents, identify relevant laws and precedents, and even generate drafts for simple contracts and agreements.
While AI will eliminate many routine tasks performed by paralegals, the demand for legal professionals will still exist, particularly for complex cases, client consultations, and courtroom representation.
8. Accountants
While AI is already being used in accounting to automate bookkeeping, tax filing, and financial reporting, it is expected to take on an even larger role in the near future. AI systems can analyze vast amounts of financial data, detect fraud, and generate real-time reports, reducing the need for traditional accounting work.
However, accountants who specialize in more complex financial tasks, such as advising clients, tax planning, and financial strategy, will continue to be in demand.